Posts by yoga@nexus-analytics.co.id
Oxygen, CO2, and O2 Analyzer
O2, CO2, and N2 analyzer Systech Illinois’ O2, CO2, and N2 analyzer is a cutting-edge solution designed to provide precise measurements of oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2) levels in various industrial and laboratory environments. This state-of-the-art instrument offers unparalleled accuracy and reliability, making it an essential tool for quality control and process…
Read MoreWEBINAR 08 : Measurement of Nanoparticle Size Distribution & Microrheology by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Zeta Potential by Phase Analysis Light Scattering (PALS), and Molecular Weight by Static Light Scattering (SLS) using BeNano Bettersize Instruments.
About Nexus Analytics Indonesia
Nexus Analytics Group, which includes Nexus Analytics Malaysia, Nexus Analytics Singapore, Team Medical & Scientific Sdn BHD, and, since 2023, Nexus Analytics Indonesia, became part of the larger Melchers Group family after being acquired in 2017. With a strong presence across Southeast Asia, Nexus Analytics Group is recognized as a leader in scientific research product…
Read MoreWebinar 02 : Fast and Easy Multi-Elemental Chemical Analysis With Lase-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
Highlight Webinar : Introduction to LIBS: Brief overview of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Explanation of how LIBS works and its applications in chemical analysis. Advantages of LIBS: Highlight the advantages of LIBS over traditional chemical analysis methods. Discuss its rapid analysis capabilities and minimal sample preparation requirements. Applications of LIBS: Explore the diverse range of…
Read MoreWebinar 01 : Pengenalan Nano Particle Tracking Analysis (NTA) dan Aplikasinya – Particle Metrix
Highlight Webinar : Introduction to NTA: NTA is a technique used for the visualization and analysis of nanoparticles in various solutions. It employs light scattering and Brownian motion principles to track and analyze particles in real-time. Principles of NTA: NTA utilizes laser light to illuminate nanoparticles suspended in a liquid medium. Brownian motion causes the…
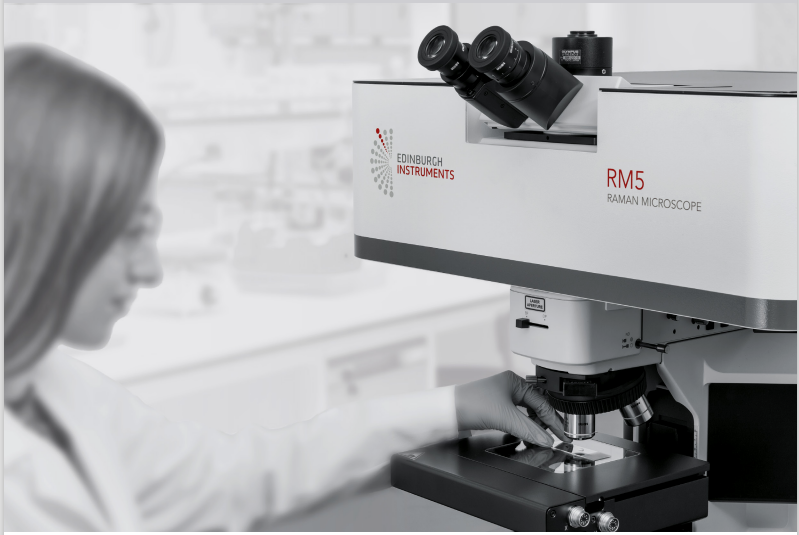
Read MoreRaman Microscope & Photoluminesence (Spectrofluorometer)
A Raman microscope and a photoluminescence spectrofluorometer are both sophisticated analytical instruments used in materials science, chemistry, biology, and other scientific fields for studying the properties of materials at the molecular level. Here’s a brief overview of each: Both Raman microscopy and photoluminescence spectroscopy offer valuable insights into the properties and behavior of materials at…
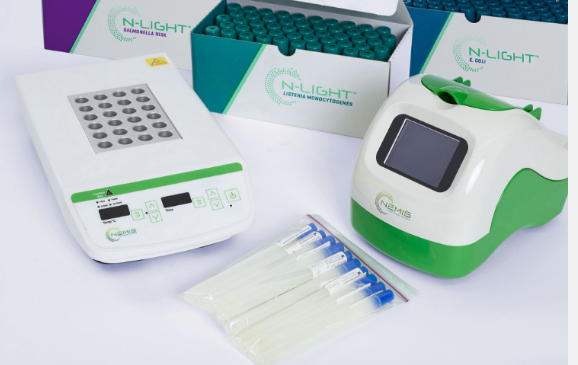
Read MorePathogen Bacteria Analyzer
pathogen bacteria analyzers is quite common in the field of microbiology and biotechnology. These devices are typically designed to rapidly detect and identify pathogenic bacteria in various samples, including food, water, clinical specimens, and environmental samples. Features of such analyzers may include:
Read MoreNuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure, dynamics, and interactions of molecules, primarily in the liquid phase. It exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei, particularly hydrogen (^1H) and carbon (^13C), which are abundant in organic molecules. Here’s a brief overview of how NMR works: NMR spectroscopy…
Read MoreNano Tracking Analyzer (NTA)
A Nano Tracking Analyzer (NTA) is a sophisticated instrument used for the characterization and analysis of nanoparticles in liquid suspensions. Utilizing advanced optical microscopy techniques, the NTA enables real-time visualization and measurement of nanoparticles with high resolution and sensitivity. Applications of Nano Tracking Analyzers span various fields, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, nanotechnology, environmental science, and materials…
Read MoreHigh Pressure Homogenizer
HOMOGENIZER A high-pressure homogenizer is an advanced device used in various industries for the precise and efficient processing of fluids, emulsions, and suspensions. It operates by forcing a fluid mixture through a narrow channel or valve at extremely high pressures, typically ranging from 1000 to 2000 bar (14,500 to 29,000 psi). This intense pressure disrupts…
Read More